Bole, Ghana
Bole | |
|---|---|
District Capital | |
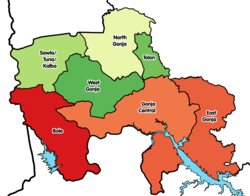
Location of Bole in Savannah region | |
| Coordinates: 9°2′N 2°29′W / 9.033°N 2.483°W | |
| Country | Ghana |
| Region | Savannah Region |
| District | Bole District |
| Population (2013) | |
| • Total | — |
| Time zone | GMT |
| • Summer (DST) | GMT |
Bole is a small town and is the capital of Bole district, a district in the Savannah Region of northern Ghana.[1] Bole is connected by road to the town of Sawla and the town of Bamboi. Bole is home to the Bole District Hospital and post office.[1] The Bole District covers an area of 4800 km2 land mass and has a population of about 87,656.[2]
History
[edit]Bole was founded as a trading center by Soninke Wangara immigrants, the same group that were the progenitors of the Dyula of Begho, Bouna, Bondoukou and Kong.[3] The town was located on an important regional trade route for kola nuts linking the Manding region with Hausaland. In 1818 Bole fought a war against the Ashanti Empire. When they lost, the victors deposed the ruling Timite family of imams and replaced them with the Kamaghate.[4]
Institutions
[edit]- Bole Senior High School[5]
- Bole District Police Command[6]
- Bole District Government Hospital[6]
- Nkilgi FM[7]
Notable natives
[edit]Climate
[edit]| Climate data for Bole (1991–2020) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 39.6 (103.3) |
41.5 (106.7) |
41.5 (106.7) |
41.0 (105.8) |
38.5 (101.3) |
36.1 (97.0) |
34.4 (93.9) |
34.0 (93.2) |
33.8 (92.8) |
36.0 (96.8) |
38.1 (100.6) |
39.0 (102.2) |
41.5 (106.7) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 35.5 (95.9) |
37.0 (98.6) |
37.0 (98.6) |
35.0 (95.0) |
33.2 (91.8) |
31.2 (88.2) |
29.7 (85.5) |
29.2 (84.6) |
30.2 (86.4) |
32.2 (90.0) |
34.3 (93.7) |
35.1 (95.2) |
33.3 (91.9) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 26.8 (80.2) |
29.1 (84.4) |
30.4 (86.7) |
29.6 (85.3) |
28.3 (82.9) |
26.8 (80.2) |
25.7 (78.3) |
25.4 (77.7) |
25.9 (78.6) |
26.9 (80.4) |
27.0 (80.6) |
26.2 (79.2) |
27.3 (81.1) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 18.1 (64.6) |
21.1 (70.0) |
23.7 (74.7) |
24.1 (75.4) |
23.4 (74.1) |
22.4 (72.3) |
21.8 (71.2) |
21.6 (70.9) |
21.5 (70.7) |
21.6 (70.9) |
19.7 (67.5) |
17.3 (63.1) |
21.4 (70.5) |
| Record low °C (°F) | 11.0 (51.8) |
13.5 (56.3) |
15.6 (60.1) |
19.2 (66.6) |
19.2 (66.6) |
18.7 (65.7) |
18.7 (65.7) |
18.0 (64.4) |
17.2 (63.0) |
15.0 (59.0) |
9.5 (49.1) |
10.1 (50.2) |
9.5 (49.1) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 3.2 (0.13) |
15.9 (0.63) |
46.0 (1.81) |
104.7 (4.12) |
128.9 (5.07) |
139.6 (5.50) |
137.2 (5.40) |
155.4 (6.12) |
198.7 (7.82) |
111.0 (4.37) |
18.5 (0.73) |
4.2 (0.17) |
1,063.3 (41.86) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 1.0 mm) | 0.2 | 1.0 | 3.5 | 6.3 | 8.5 | 9.5 | 9.2 | 9.9 | 14.1 | 9.0 | 1.8 | 0.3 | 73.3 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 255.0 | 228.2 | 228.2 | 225.0 | 232.8 | 180.3 | 151.5 | 133.0 | 155.2 | 230.1 | 243.9 | 244.1 | 2,507.3 |
| Source: NOAA[8] | |||||||||||||
References
[edit]- ^ a b "Bole District". Ghana Districts. 3 May 2008. Archived from the original on 14 June 2013. Retrieved 19 January 2024.
- ^ "Bole". mofa.gov.gh. Retrieved 2022-06-12.
- ^ Massing, Andrew (2000). "The Wangara, an Old Soninke Diaspora in West Africa?". Cahiers d'Études Africaines. 40 (158): 294. doi:10.4000/etudesafricaines.175. JSTOR 4393041. Retrieved 24 May 2024.
- ^ Massing, Andrew (2012). "Imams of Gonja The Kamaghate and the Transmission of Islam to the Volta Basin". Cahiers d'Études Africaines. 52 (205): 75-85. JSTOR 41446033. Retrieved 24 May 2024.
- ^ "Assistant Headmaster of Bole SHS arrested for alleged rape". Graphic Online. Retrieved 2022-05-27.
- ^ a b www.3news .com (2022-05-25). "Bole SHS Asst. Head accused of raping final-year student". 3NEWS.com. Retrieved 2022-05-27.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ Agyeman, Adwoa (2022-04-11). "Bole SHS old students stop auctioning of school bus". Adomonline.com. Retrieved 2022-05-27.
- ^ "Bole Normals 1991–2020". World Meteorological Organization Climatological Standard Normals (1991–2020). National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Archived from the original on 29 September 2023. Retrieved 29 September 2023.